
Dead space ventilation promotes alveolar hypocapnia reducing surfactant secretion by altering mitochondrial function.
Kiefmann M, Tank S, Tritt MO, Keller P, Heckel K, Schulte-Uentrop L, Olotu C, Schrepfer S, Goetz AE, Kiefmann R. Strategies for recruitment and retention of underrepresented populations with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease for a clinical trial. Huang B, De Vore D, Chirinos C, Wolf J, Low D, Willard-Grace R, Tsao S, Garvey C, Donesky D, Su G, Thom DH. Respiratory Mechanics, Lung Recruitability, and Gas Exchange in Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.

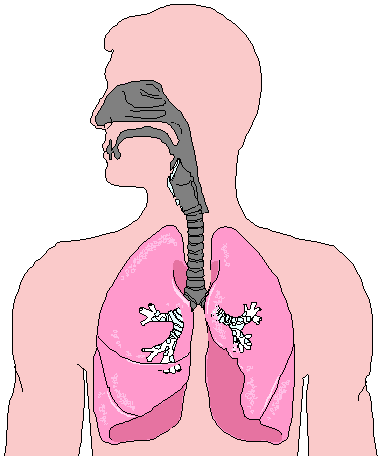
One can see an increase in the value of physiologic dead space in lung disease states where the diffusion membrane of alveoli does not function properly or when there are ventilation/perfusion mismatch defects.Ĭopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.Ĭoppola S, Froio S, Marino A, Brioni M, Cesana BM, Cressoni M, Gattinoni L, Chiumello D. Therefore, physiologic dead space is equivalent to anatomical. In a healthy adult, alveolar dead space can be considered negligible. The respiratory zone is comprised of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar duct, alveolar sac, and alveoli. Physiologic or total dead space is equal to anatomic plus alveolar dead space which is the volume of air in the respiratory zone that does not take part in gas exchange.

This volume is considered to be 30% of normal tidal volume (500 mL) therefore, the value of anatomic dead space is 150 mL. Anatomical dead space is represented by the volume of air that fills the conducting zone of respiration made up by the nose, trachea, and bronchi. The two types of dead space are anatomical dead space and physiologic dead space. Dead space represents the volume of ventilated air that does not participate in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
